可视化回归测试
Vitest 原生支持可视化回归测试。它会自动截取 UI 组件或页面的截图,并与基准图像对比,以捕捉那些非预期的视觉变化。
与只验证功能逻辑的功能测试不同,可视化测试能发现样式异常、布局偏移和渲染错误——这些问题如果没有细致的人工检查,往往会被忽略。
为什么需要可视化回归测试?
视觉 bug 不会报错,但它们的外观已经改变。这正是可视化测试的意义所在:
- 按钮依然能提交表单,但颜色却变成了亮粉色
- 文本在桌面端显示正常,在移动端却被挤压变形
- 功能没问题,可两个容器已跑出视口
- 精心的 CSS 重构完成了,却破坏了某个无人测试的页面布局
可视化回归测试是 UI 的安全网,确保这些变化在进入生产环境之前就被自动发现并处理。
快速入门
浏览器渲染差异
可视化回归测试对运行环境非常敏感,不同机器生成的截图可能存在差异,常见原因包括:
- 字体渲染差异(最常见,Windows、macOS、Linux 各不相同)
- GPU 驱动与硬件加速
- 是否使用无头模式
- 浏览器版本与设置
- 甚至偶发的系统差异...
因此,Vitest 会在截图文件名中添加浏览器和平台信息(如 button-chromium-darwin.png),避免不同环境的截图互相覆盖。
要获得稳定结果,应使用相同的测试环境。推荐采用云端服务(如 Azure App Testing)或基于 Docker containers 的环境。
在 Vitest 中,可通过 toMatchScreenshot assertion 断言运行可视化回归测试:
import { expect, test } from 'vitest'
import { page } from 'vitest/browser'
test('hero section looks correct', async () => {
// ...the rest of the test
// capture and compare screenshot
await expect(page.getByTestId('hero')).toMatchScreenshot('hero-section')
})创建基准截图
首次运行可视化测试时, Vitest 会生成一张基准( baseline )截图,并提示如下错误信息使测试失败:
expect(element).toMatchScreenshot()
No existing reference screenshot found; a new one was created. Review it before running tests again.
Reference screenshot:
tests/__screenshots__/hero.test.ts/hero-section-chromium-darwin.png确认截图正确后再次运行测试,Vitest 会将后续结果与该基准图比较。
TIP
基准截图存放在测试文件所在目录下的 __screenshots__ 文件夹中, 请务必提交到版本库。
截图组织方式
Vitest 默认将截图按以下结构保存:
.
├── __screenshots__
│ └── test-file.test.ts
│ ├── test-name-chromium-darwin.png
│ ├── test-name-firefox-linux.png
│ └── test-name-webkit-win32.png
└── test-file.test.ts文件名由三部分组成:
- 测试名:来自
toMatchScreenshot()的第一个参数,或自动根据测试用例名生成 - 浏览器名:
chrome、chromium、firefox、webkit - 平台:如
aix、darwin、linux、win32等
这种命名方式可避免不同环境生成的截图互相覆盖。
更新基准截图
当你有意修改 UI 时,需要更新基准截图:
$ vitest --update提交前务必核对更新后的截图,确保改动符合预期。
可视化测试的工作原理
可视化回归测试需要稳定的截图进行比较。但页面不会立即稳定,图片加载、动画完成、字体渲染和布局稳定都需要时间。
Vitest 通过 “稳定截图检测” 机制自动处理这一问题:
- Vitest 首先拍摄初始截图(或使用现有参考截图)作为基准
- 再次拍摄截图并与基准比对
- 如果截图一致,判定页面已稳定并继续测试
- 如果存在差异,则将最新截图设为新基准并重复流程
- 这会持续进行,直到达到稳定性或超时
此机制确保临时性视觉变化(如加载动画)不会引发误报。但对于持续动画元素,系统会因超时而终止,建议测试期间 禁用动画。
当经过重试(一次或多次)获得稳定截图且存在参考截图时,Vitest 会使用 createDiff: true 参数执行最终比对。若结果不匹配,将生成差异图像。
在稳定性检测阶段,Vitest 调用比对器时使用 createDiff: false 参数,因此仅需判断截图是否匹配。这种优化使检测过程保持高效。
配置可视化测试
全局配置
可在 Vitest 配置文件 中设定可视化回归测试的默认规则:
import { defineConfig } from 'vitest/config'
export default defineConfig({
test: {
browser: {
expect: {
toMatchScreenshot: {
comparatorName: 'pixelmatch',
comparatorOptions: {
// 0-1,表示允许的颜色差异阈值
threshold: 0.2,
// 允许 1% 的像素存在差异
allowedMismatchedPixelRatio: 0.01,
},
},
},
},
},
})单测试配置
若某个测试需要不同的比较标准,可在调用时覆盖全局设置:
await expect(element).toMatchScreenshot('button-hover', {
comparatorName: 'pixelmatch',
comparatorOptions: {
// 对文字密集型元素采用更宽松的比对标准
allowedMismatchedPixelRatio: 0.1,
},
})最佳实践
聚焦测试目标元素
除非确实需要测试整个页面,否则应优先只对目标组件截图,这能显著减少因页面其他部分变化而造成的误报。
// ❌ 捕获整个页面;容易受到无关更改的影响
await expect(page).toMatchScreenshot()
// ✅ 仅捕获被测试的组件
await expect(page.getByTestId('product-card')).toMatchScreenshot()处理动态内容
测试中,如果页面包含诸如时间戳、用户信息或随机值等动态内容,往往会导致结果不一致而造成测试失败。 解决方法有两种:一是模拟这些动态数据的生成源; 二是在使用 Playwright 进行截图时,在 screenshotOptions 中启用 mask 选项, 将这些动态区域遮盖,从而确保测试结果的稳定性。
await expect(page.getByTestId('profile')).toMatchScreenshot({
screenshotOptions: {
mask: [page.getByTestId('last-seen')],
},
})禁用所有动画
动画效果往往会导致测试结果出现波动。为避免这种情况, 可以在测试执行过程中注入一段自定义的 CSS 样式代码,用于禁用所有动画,从而提升测试的稳定性。
*, *::before, *::after {
animation-duration: 0s !important;
animation-delay: 0s !important;
transition-duration: 0s !important;
transition-delay: 0s !important;
}TIP
在使用 Playwright 作为测试工具时,若执行断言操作,动画会被自动禁用。 具体而言,screenshotOptions 配置中的 animations 选项会默认设为 "disabled",从而确保截图与测试结果的稳定一致。
设置合理的阈值
在视觉回归测试中,阈值调整是一项需要权衡的工作——它取决于页面内容、测试环境、 应用所能容忍的差异范围,且可能因具体测试而有所不同。
Vitest 并未为像素差异设定默认阈值,这需要由用户根据实际需求来决定。 官方建议使用 allowedMismatchedPixelRatio,让阈值按截图的整体尺寸比例计算,而非依赖固定像素数量。
当 allowedMismatchedPixelRatio 与 allowedMismatchedPixels 同时设置时, Vitest 会优先采用二者中限制更严格的那一个,以确保测试结果的准确性与一致性。
保持统一的视口大小
浏览器实例的默认窗口尺寸可能存在差异,这会影响视觉回归测试的稳定性。为避免由于尺寸不一致而产生的截图偏差, 建议在测试脚本或浏览器实例配置中显式指定一个固定的视口大小,从而确保测试结果的可重复性与一致性。
await page.viewport(1280, 720)import { playwright } from '@vitest/browser-playwright'
import { defineConfig } from 'vitest/config'
export default defineConfig({
test: {
browser: {
enabled: true,
provider: playwright(),
instances: [
{
browser: 'chromium',
viewport: { width: 1280, height: 720 },
},
],
},
},
})使用 Git LFS 管理基准截图
对于规模较大的视觉回归测试套件,建议将基准截图文件存储在 Git LFS 中。 这样既能避免仓库体积膨胀,又能高效管理和传输这些大尺寸文件,提升团队协作效率。
调试视觉测试失败
当视觉回归测试未能通过时, Vitest 会生成三张关键截图,帮助你分析问题所在:
- 参考截图( Reference screenshot ):测试期望的基准图像
- 实际截图( Actual screenshot ):测试运行过程中截取的画面
- 差异图( Diff image ):用高亮标记出参考图与实际图的差异(有时可能不会生成)
在调试时,你会在输出中看到类似如下的文件列表或路径信息:
expect(element).toMatchScreenshot()
Screenshot does not match the stored reference.
245 pixels (ratio 0.03) differ.
Reference screenshot:
tests/__screenshots__/button.test.ts/button-chromium-darwin.png
Actual screenshot:
tests/.vitest-attachments/button.test.ts/button-chromium-darwin-actual.png
Diff image:
tests/.vitest-attachments/button.test.ts/button-chromium-darwin-diff.png如何解读差异图
- 红色像素:表示参考截图与实际截图之间存在显著差异的区域
- 黄色像素:由抗锯齿处理带来的细微差异(仅在未忽略抗锯齿时可见)
- 透明或原始图像部分:表示两张截图在该区域完全一致
TIP
如果差异图几乎被红色覆盖,说明测试结果与预期严重不符,需要重点排查。 若只是文字边缘零星出现少量红点,可能只是渲染细节差异,此时适当提高阈值即可解决。
常见问题与解决方案
字体渲染引发的误报
由于不同操作系统在字体可用性与渲染方式上差异明显,视觉回归测试中可能会出现“误报”现象。为降低这种风险,可以考虑以下做法:
使用 Web 字体,并在测试执行前等待字体完全加载;
ts// wait for fonts to load await document.fonts.ready // continue with your tests对包含大量文字的区域适当提高像素差异的比较阈值,以减少因字体渲染细微差别导致的误报;
tsawait expect(page.getByTestId('article-summary')).toMatchScreenshot({ comparatorName: 'pixelmatch', comparatorOptions: { // 10% of the pixels are allowed to change allowedMismatchedPixelRatio: 0.1, }, })使用云端服务或容器化测试环境,确保字体渲染效果在各次测试中保持一致,从而减少系统差异带来的影响;
测试不稳定或截图尺寸不一致
如果测试结果出现随机通过或失败,或者在不同运行中生成的截图尺寸不一致,可以采取以下措施:
- 确保页面所有内容均已加载完成,包括加载指示器与动画;
- 明确设置固定的视口大小,例如:
await page.viewport(1920, 1080); - 检查页面在视口临界尺寸下的响应式布局表现;
- 排查是否存在非预期的动画或过渡效果干扰截图结果;
- 对体积较大的截图适当延长测试的超时时间;
- 使用云端服务或容器化环境,确保字体渲染、浏览器配置等保持一致。
团队版视觉回归测试方案
视觉回归测试对环境的稳定性要求极高,而本地开发机并不适合担当这一角色。
在团队协作中,常见的三种方案是:
- 自托管运行器:部署过程复杂,日常维护工作量大;
- GitHub Actions:对开源项目免费,可与任何测试框架或服务集成;
- 云服务:如 Microsoft Playwright Testing,专为解决视觉测试环境一致性问题而构建。
我们将重点介绍第 2 和第 3 种方案,因为它们能最快投入使用。
主要权衡点在于:
- GitHub Actions:视觉测试只能在持续集成(CI)环境中运行,开发者无法直接在本地执行;
- Microsoft 云服务:可在任意环境运行,但需额外付费,并且仅支持 Playwright。
要点在于,将视觉回归测试与常规测试分离运行。 否则,你可能会因截图差异引发的失败日志而浪费数小时进行排查。
测试组织建议
首先,应将视觉回归测试与其他测试隔离管理。 建议单独建立一个 visual 文件夹(或根据项目结构选择更合适的目录名称)来存放这些测试用例,以便维护与执行。
{
"scripts": {
"test:unit": "vitest --exclude tests/visual/*.test.ts",
"test:visual": "vitest tests/visual/*.test.ts"
}
}这样,开发者就能在本地运行 npm run test:unit ,而无需受到视觉回归测试的影响; 视觉测试则放在环境一致的持续集成( CI )平台中运行,以确保结果稳定可靠。
持续集成( CI )环境配置
在 CI 环境中运行视觉回归测试时,需要确保浏览器已正确安装。至于如何安装,则取决于你所使用的 CI 服务提供商及其运行环境。
Playwright 能让浏览器安装与管理变得非常简单。 你只需固定所用的 Playwright 版本,并在运行测试之前加入以下命令或脚本:
# ...the rest of the workflow
- name: Install Playwright Browsers
run: npx --no playwright install --with-deps --only-shell最后,运行你的视觉回归测试:
# ...the rest of the workflow
# ...browser setup
- name: Visual Regression Testing
run: npm run test:visual更新工作流程
关键点来了——切勿在每一次 Pull Request 中都自动更新截图, (那只会带来混乱)。更稳妥的方式,是建立一个手动触发的工作流程, 让开发者在有意更改 UI 时主动运行,从而更新基准截图。
该工作流程具备以下特性:
- 仅在功能分支上运行,确保主分支安全不受影响;
- 自动将触发流程的开发者署名为共同作者;
- 阻止同一分支上的并发执行,避免冲突与资源浪费;
- 生成一份清晰美观的执行摘要,便于快速查看结果。
当基准截图发生变动时,系统会列出所有具体的变化项,方便开发者快速了解差异。
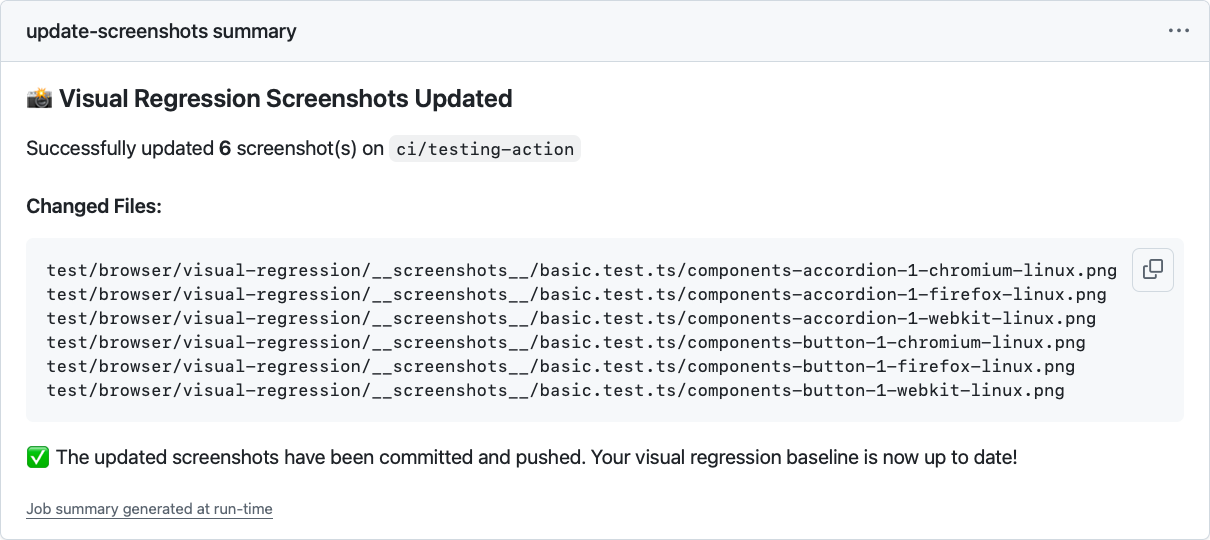
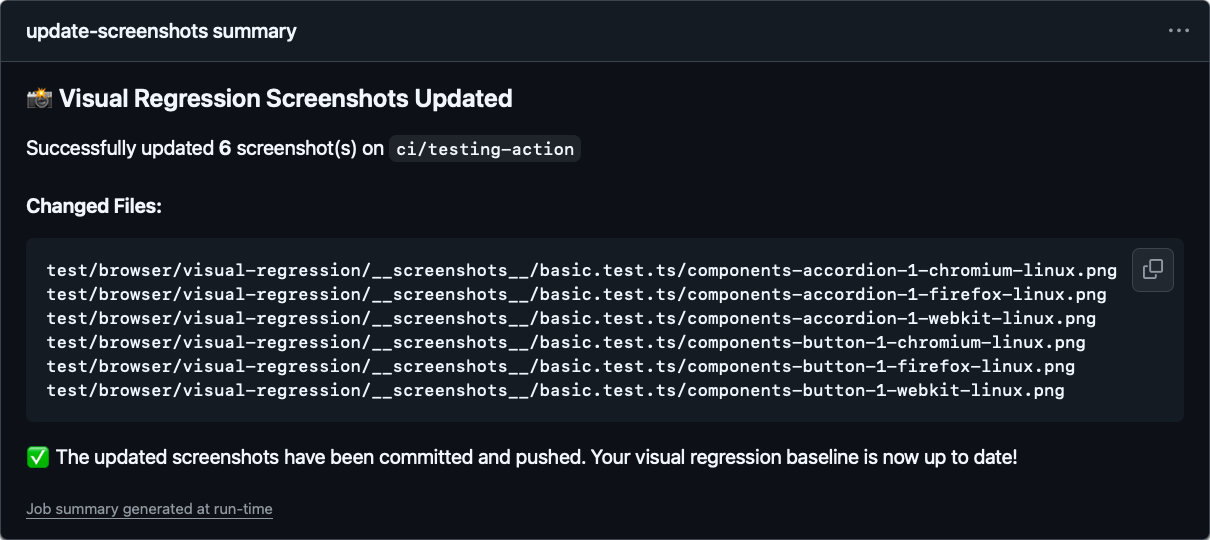
当没有任何变化时,系统同样会明确提示,让你一目了然。
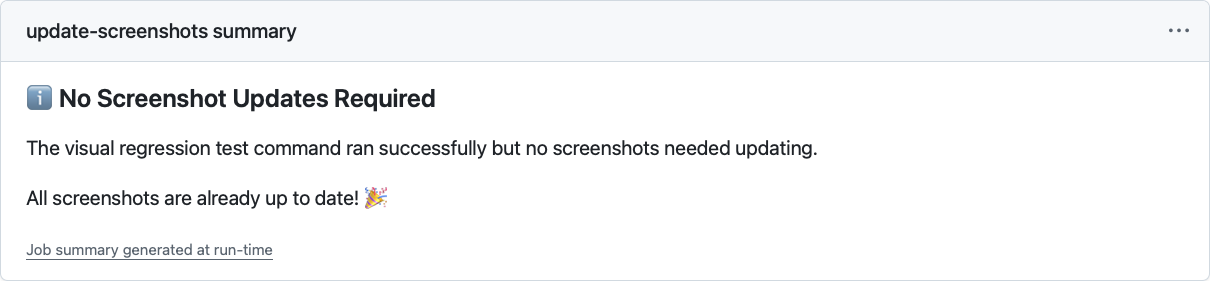
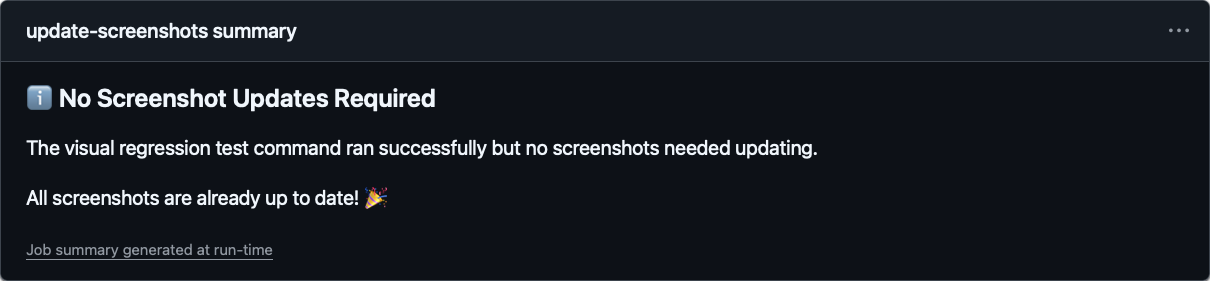
TIP
这只是实现的其中一种方式。 有些团队倾向于在 Pull Request 中添加特定评论(如 /update-screenshots)来触发更新, 也有团队通过添加标签来完成这一操作。 你可以根据自身的开发流程进行调整。
关键在于,必须建立一种可控的机制来更新基准截图, 以避免不必要的混乱和错误。
name: Update Visual Regression Screenshots
on:
workflow_dispatch: # manual trigger only
env:
AUTHOR_NAME: 'github-actions[bot]'
AUTHOR_EMAIL: '41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com'
COMMIT_MESSAGE: |
test: update visual regression screenshots
Co-authored-by: ${{ github.actor }} <${{ github.actor_id }}+${{ github.actor }}@users.noreply.github.com>
jobs:
update-screenshots:
runs-on: ubuntu-24.04
# safety first: don't run on main
if: github.ref_name != github.event.repository.default_branch
# one at a time per branch
concurrency:
group: visual-regression-screenshots@${{ github.ref_name }}
cancel-in-progress: true
permissions:
contents: write # needs to push changes
steps:
- name: Checkout selected branch
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
ref: ${{ github.ref_name }}
# use PAT if triggering other workflows
# token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Configure Git
run: |
git config --global user.name "${{ env.AUTHOR_NAME }}"
git config --global user.email "${{ env.AUTHOR_EMAIL }}"
# your setup steps here (node, pnpm, whatever)
- name: Setup Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 24
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Install Playwright Browsers
run: npx --no playwright install --with-deps --only-shell
# the magic happens below 🪄
- name: Update Visual Regression Screenshots
run: npm run test:visual --update
# check what changed
- name: Check for changes
id: check_changes
run: |
CHANGED_FILES=$(git status --porcelain | awk '{print $2}')
if [ "${CHANGED_FILES:+x}" ]; then
echo "changes=true" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "Changes detected"
# save the list for the summary
echo "changed_files<<EOF" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "$CHANGED_FILES" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "EOF" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "changed_count=$(echo "$CHANGED_FILES" | wc -l)" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
else
echo "changes=false" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "No changes detected"
fi
# commit if there are changes
- name: Commit changes
if: steps.check_changes.outputs.changes == 'true'
run: |
git add -A
git commit -m "${{ env.COMMIT_MESSAGE }}"
- name: Push changes
if: steps.check_changes.outputs.changes == 'true'
run: git push origin ${{ github.ref_name }}
# pretty summary for humans
- name: Summary
run: |
if [[ "${{ steps.check_changes.outputs.changes }}" == "true" ]]; then
echo "### 📸 Visual Regression Screenshots Updated" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "Successfully updated **${{ steps.check_changes.outputs.changed_count }}** screenshot(s) on \`${{ github.ref_name }}\`" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "#### Changed Files:" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "\`\`\`" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "${{ steps.check_changes.outputs.changed_files }}" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "\`\`\`" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "✅ The updated screenshots have been committed and pushed. Your visual regression baseline is now up to date!" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
else
echo "### ℹ️ No Screenshot Updates Required" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "The visual regression test command ran successfully but no screenshots needed updating." >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
echo "All screenshots are already up to date! 🎉" >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
fi该选哪一个?
两种方案都可行,关键在于团队最在意的痛点是什么。
如果你的团队已经深度依赖 GitHub 生态,那么 GitHub Actions 几乎是无可替代的选择——对开源项目免费、 支持任意浏览器服务商、并且可完全掌控执行流程。
缺点在于:当有人在本地生成的截图与 CI 环境的基准不一致时,就会出现那句熟悉的 “在我机器上没问题”。
如果团队需要在本地执行视觉回归测试,那么云服务或许更适合。 这种方式特别适合有设计师参与审核,或开发者希望在推送代码前发现并修复问题的团队, 能够跳过 “推送—等待—检查—修改—再推送” 的繁琐循环。
如果依然犹豫,不妨先从 GitHub Actions 开始;等到本地测试成为痛点时,再引入云服务也不迟。