快速 · 轻量 · 深度集成
基于 Vite 驱动
可以复用 Vite 的配置和插件,使得应用和测试保持一致。但是使用 Vitest 并不需要使用 Vite!
与 Jest 兼容
支持 Expect 断言、快照测试、覆盖率等功能,从 Jest 迁移过来非常简单。

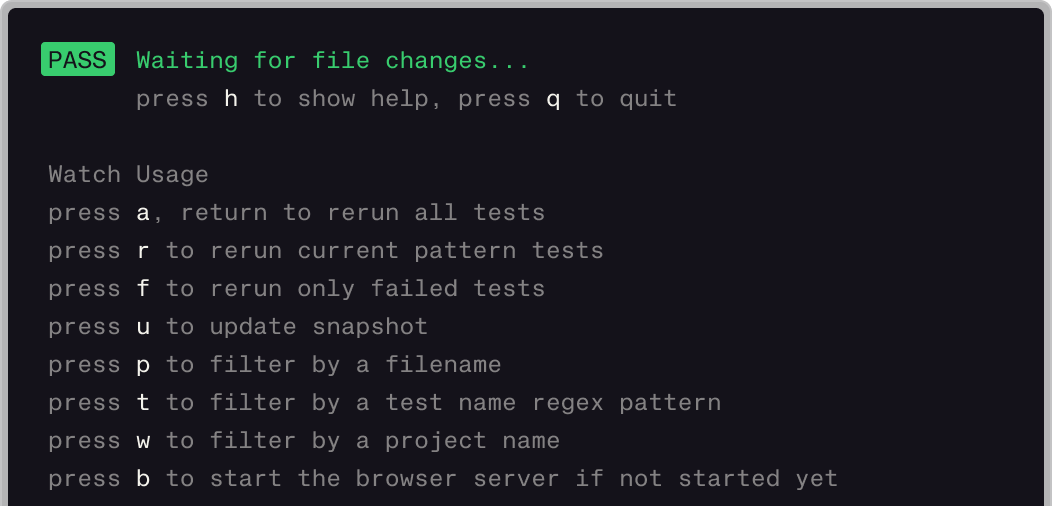
智能且即时的 watch 模式
只重新运行相关的更改,就像测试的热模块重载一样!
ESM、TypeScript、JSX 支持
内置 ESM、TypeScript 和 JSX 支持,由 Oxc 驱动。
可以复用 Vite 的配置和插件,使得应用和测试保持一致。但是使用 Vitest 并不需要使用 Vite!
支持 Expect 断言、快照测试、覆盖率等功能,从 Jest 迁移过来非常简单。

只重新运行相关的更改,就像测试的热模块重载一样!

内置 ESM、TypeScript 和 JSX 支持,由 Oxc 驱动。